- Blog
- 9 Great Behavioral Segmentation Examples for 2025
9 Great Behavioral Segmentation Examples for 2025
-
Nikolett Lorincz
- Marketing
- 6 min read
Table of Contents
Customers expect personalization on your website. In fact, 74% of customers feel frustrated when website content is not personalized.
To customize each shopper’s unique experience, you need to rely on segmentation, which involves categorizing your customers based on particular characteristics or customer behavior.
In this post, we’ll explore some of the best behavioral segmentation methods to help you better understand and meet your customers’ needs.
We’ll discuss the different types of behavioral segmentation, such as purchase behavior, occasion-based purchases, benefits sought, and customer loyalty. By leveraging these strategies, you can enhance personalization, improve customer satisfaction, and drive more conversions.
Let’s get started!
What is behavioral segmentation?
Behavioral segmentation categorizes your visitors into groups based on a shared, specific behavior pattern like:
- Their purchasing behavior: For example, do they buy at the same time of year? Understanding customer purchases helps analyze the factors and behaviors that lead to buying decisions.
- The customer journey: Whether they’re considering making a purchase or they’ve just bought.
- The awareness stage: For example, they may be product-aware and compare your product with other options.
- Their knowledge: What do they know about your brand and products?
- Product usage: How do they use your product?
The aim of behavioral segmentation is to:
- Understand the desires of different kinds of customers
- Match your product based on your customers’ wants and needs
- Find opportunities to optimize the customer journey
- Create a targeted, personalized marketing strategy to draw in your customers and build customer loyalty
Now that we know what behavioral segmentation is, let’s have a look at why it’s important.
Why is behavioral segmentation important?
When you understand your customers better, you can provide them with tailored and personalized experiences.
Let’s take a look at how this directly affects your marketing.
- Level up your customers’ personalized experiences: This helps you to understand how to target different customer groups with customized offers on their preferred channels. It gives you a better chance to nurture them further into the customer journey.
- Predict and influence customer behavior: Understanding patterns in customer behavior helps you predict future actions and influence purchasing decisions through targeted campaigns.
- Identify the best prospects: You’ll be able to identify which prospects add the most value to your business. It can save you time and resources.
9 behavioral segmentation examples
Now that we’ve discussed the basics, let’s get into some practical examples of behavioral segments in ecommerce.
1. Purchasing behavior
Segmenting your customers based on their purchasing behavior can tell you more about their decision-making process. You can understand:
- What customers consider before purchasing. Do they talk to friends? Weigh up prices? Read reviews?
- The complex layers of decision-making. What factors influence their decision most? A great deal? Brand perception? The time of year, e.g. Christmas?
- The barriers (obvious and non-obvious) to making a purchase. Think: expense, need, inertia (the effort it takes to buy).
- Which behaviors will lead to a purchase or not? Understanding these behaviors can help in increasing customer lifetime value by tailoring strategies to retain customers and maximize their long-term revenue potential.
Let’s take a look at this in more detail. You can break purchasing behavior down into some general categories:
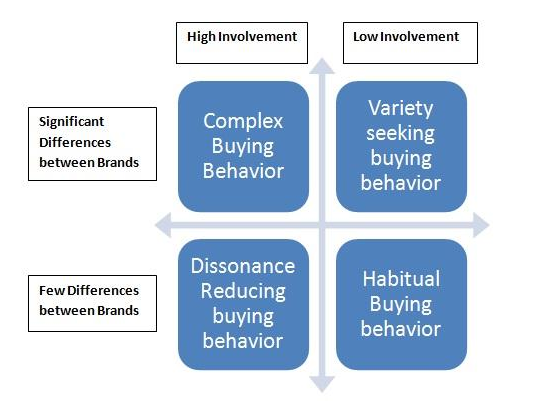
Source: Clootrack
Now let’s take a look at this in more detail.
Complex buying behavior: It happens when people are about to make an expensive purchase. They are super involved, and doing a ton of research. Cars, homes, and real estate insurance and pet insurance policies are some examples that come to mind when we think of a complex purchase decision.
Dissonance reducing buying behavior: The buyer involvement here is also very high. They may talk it through with friends and family or read many reviews. But there are fewer choices therefore limited decision making. For example, if a customer is looking for a collapsible table for their camping trip, the key criteria will be the feature of the table in question and the budget for it.
Habitual buying behavior: This is where people buy stuff they use in their regular routine. Think of a toothbrush or carton of milk. Here, involvement is low and they don’t see many differences between the brands they buy from.
Variety-seeking buying behavior: Here, people see a lot of differences between brands and have a lot of options. As such, they regularly switch between different brands. They do with limited involvement, maybe switching after a friend’s recommendations or reading a couple of reviews online. You might have done this with your athletic shoes. There’s always a huge variety of new and better sneakers on the market.
2. Benefits sought
Could-be customers often value different benefits.
Take the example of skincare. Consumers who buy skincare products do so for various reasons. Here are some segmentation examples for the different benefits customers may prioritize:
- Oily skin fix
- Removes dark circles
- Smells gorgeous
- Price
- Non-irritating ingredients for sensitive skin
- Vegan or cruelty-free company ethics
See how Sephora uses a “Shop by Concern” category to learn what benefits and features are most important to each shopper.
This can help your visitors find what they’re looking for, and you can immediately know your shoppers’ concerns and the benefits they’re after.
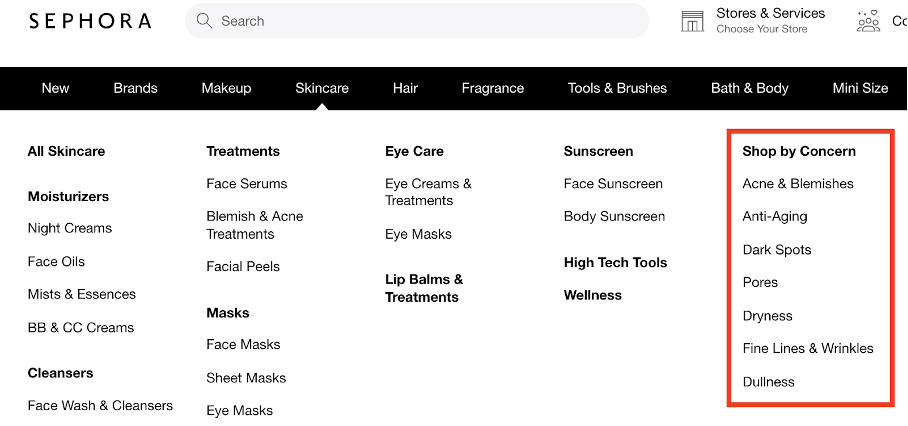
You can use this strategy on a popup too. See this example:
3. Customer journey stages
It can be tricky to pinpoint exactly where your shopper is in the customer journey. From Instagram to your homepage, your customers engage with your content at different stages across different channels.
It’s important to leverage all customer data across various touchpoints and channels to personalize messages based on their customer journey stage.
For example, you can display a personalized message like the one below for visitors in the Post-Purchase stage.
4. Usage behavior
Usage behavior looks at:
- How often existing customers use your product or service
- How they’re using it
- What features do they use the most
- How much time on average they spend using it
You can create a mind map and then segment your customers based on their usage of your product or service. The main usage segments include:
- Heavy users: These are your superfans. They’re highly engaged, spend a lot of time using your product and service, and purchase regularly.
- Medium users: They engage and purchase from time to time. Their relationship with you is often time-based or events-based (think Christmas, Cyber Monday, Black Friday, etc.).
- Light users: These customers engage with your brand, but rarely buy.
You can help turn your light users into medium and heavy users by testing different marketing strategies. Some of our fave approaches include offering prize giveaways, offering up interactive content, and offering Birthday treats like a free gift (who doesn’t love a freebie?).
5. Occasion/timing
Some occasions are universal, like booking a hotel for New Year‘s Eve. In comparison, others are personal, like buying a monthly gourmet spice subscription box filled with luxe, hard-to-find herbs and spices to keep your cooking game sharp.
In contrast, occasion-based segmentation is a common segmentation approach. This refers to when people decide to buy. Just head to your inbox and take a look at some of the emails you receive. For example, your favorite delivery service sends out coupons or flash sale emails on Fridays—people are more likely to order on the weekends.
Christmas is one of the most popular times to capitalize on occasion-based segmentation. Here’s an example of how to promote your Christmas sale:
6. Customer satisfaction
Are you accurately capturing how satisfied your customers are at every stage of their journey?
You can jump right in and fix any potential problems or address any concerns if you know how dissatisfied your customers are. In comparison, you can target highly-satisfied customers with up-sells, cross-sells, or loyalty programs.
Here’s what segmentation based on customer satisfaction could look like:

Source: Pointillist
7. Interest
You don’t have to be as high-status as Netflix or Spotify to leverage the power of smart recommendations based on your customers’ interests.
All brands should capitalize on relevant, personalized content, product, or service recommendations. Segmenting your customers in this way is a great way to drive engagement. That’s because people only see the most relevant content to them.
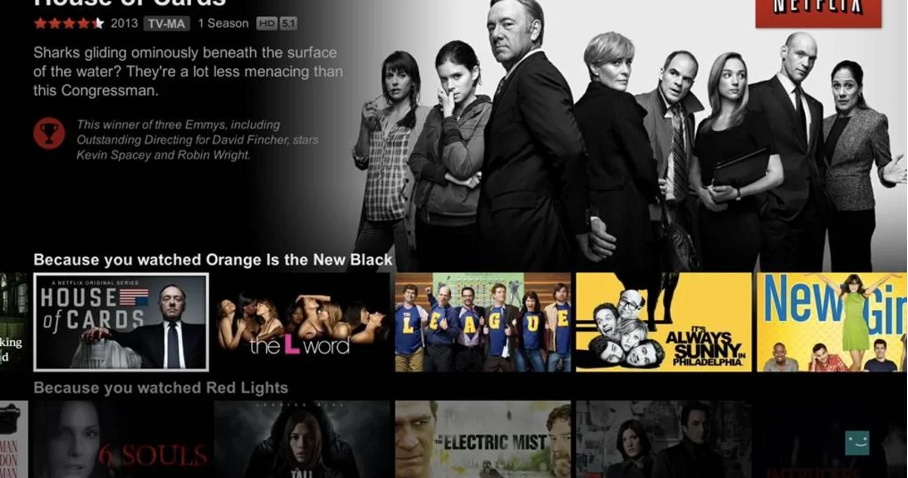
How do you go about this?
With OptiMonk, you can easily track your visitors’ behavior on your website and recommend products based on that behavior.
For example, you can recommend new items by looking at your customer’s “recently viewed products.”
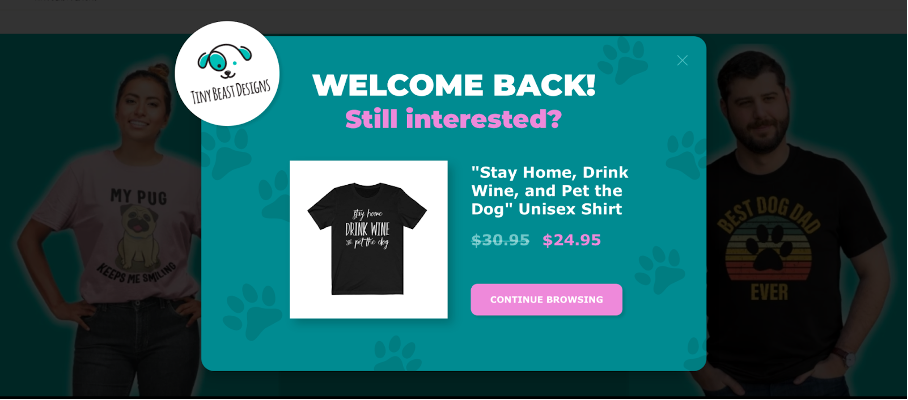
8. Engagement level
Engagement is a valuable metric for both pre-purchase and post-purchase parts of the customer journey. For example, you can use engagement-based segmentation to discover how involved different prospects behave in your pre-purchase funnel.
In addition, you can uncover how psyched people are after their initial purchase through repeat visits, purchases, or engagement with your content.
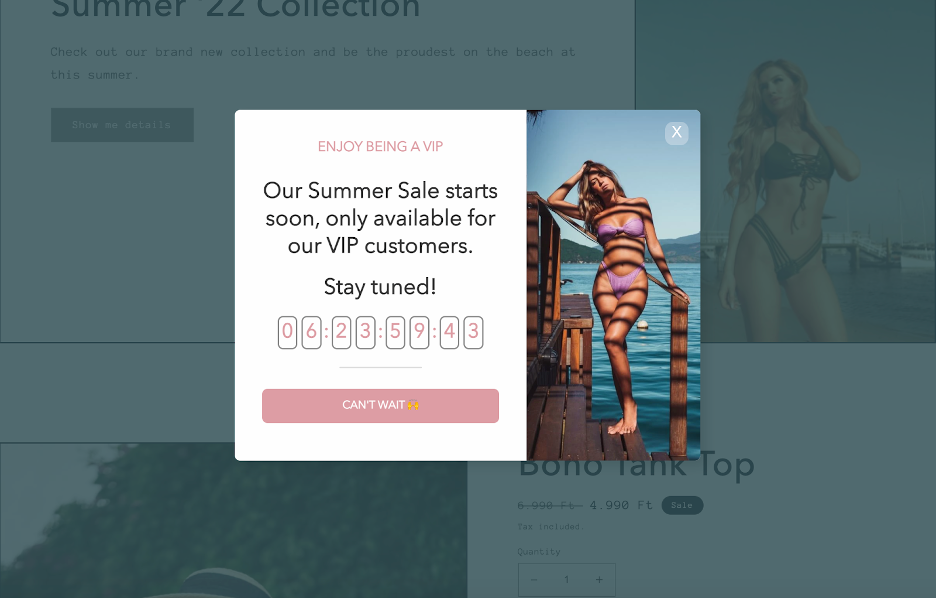
9. Customer loyalty
Understanding and leveraging customer loyalty, especially focusing on your most loyal customers, can significantly impact your business’s bottom line.
Loyal customers (or VIP customers) are those who repeatedly purchase your products or services, providing a stable revenue stream. By identifying these customers and creating tailored marketing strategies, you can enhance their experience and encourage continued loyalty.
Offering exclusive discounts, early access to new products, or personalized recommendations can make loyal customers feel valued and appreciated.
FAQ
What is an example of behavioral segmentation?
An example of behavioral segmentation is targeting frequent buyers with loyalty rewards programs. For instance, a coffee shop might offer a free drink after every ten purchases to encourage repeat visits and reward loyal customers.
How does McDonald’s use behavioral segmentation?
McDonald’s uses behavioral segmentation by analyzing customer purchase patterns and preferences. They offer different menu items based on regional tastes and create targeted promotions, like special deals during lunch hours for working professionals. Understanding the average customer’s location helps them tailor these offerings more effectively.
What are the 4 category characteristics of behavioral segmentation?
The four category characteristics of behavioral segmentation are:
- Purchase behavior: Frequency and volume of purchases.
- Benefits sought: The specific benefits customers look for in a product.
- Usage rate: How often customers use the product.
- Loyalty status: The degree of customer loyalty to the brand.
What is behavioral and psychographic segmentation?
Behavioral segmentation involves categorizing customers based on their behavior, such as purchase history and brand loyalty. Psychographic segmentation, on the other hand, classifies customers based on psychological traits, including lifestyle, values, and interests. Combining both provides a deeper understanding of customers for more effective targeting.
Wrapping up
The days of impersonalized marketing campaigns are over. People have their unique reasons for buying.
It’s up to you to decide how to effectively target your customers using demographic, psychographic, geographic, and behavioral segmentation. From the benefits of behavioral segmentation to the 4Ps of segmentation, you now have everything you need to ace marketing segmentation.
Bookmark this article and refer to it regularly as you move forward with your marketing efforts.
Migration has never been easier
We made switching a no-brainer with our free, white-glove onboarding service so you can get started in the blink of an eye.
What should you do next?
Thanks for reading till the end. Here are 4 ways we can help you grow your business:
Boost conversions with proven use cases
Explore our Use Case Library, filled with actionable personalization examples and step-by-step guides to unlock your website's full potential. Check out Use Case Library
Create a free OptiMonk account
Create a free OptiMonk account and easily get started with popups and conversion rate optimization. Get OptiMonk free
Get advice from a CRO expert
Schedule a personalized discovery call with one of our experts to explore how OptiMonk can help you grow your business. Book a demo
Join our weekly newsletter
Real CRO insights & marketing tips. No fluff. Straight to your inbox. Subscribe now
Nikolett Lorincz
- Posted in
- Marketing
Partner with us
- © OptiMonk. All rights reserved!
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
Product updates: January Release 2025








