- Blog
- A/B Testing Terminology: A Glossary for Marketers
A/B Testing Terminology: A Glossary for Marketers
-
Nikolett Lorincz
- Conversion
- 6 min read
Table of Contents
Ever felt overwhelmed by all the jargon thrown around in A/B testing discussions? You’re not alone.
A/B testing is a powerful tool for marketers, but it comes with a hefty load of terminology.
Understanding these terms is crucial for designing effective experiments and making data-driven decisions. The purpose of this guide is to demystify the key concepts you need to know so you can run A/B tests with confidence.
Let’s dive right in!
Key terminology
Knowing these terms will help you communicate more effectively with your team, interpret results accurately, and ultimately, run more successful tests.
1. A/B testing (split testing)
A/B testing, also known as split testing, is a method used to compare multiple versions of a web page or app to determine which one performs better.
By showing different versions (variants) to different segments of users, you can see which version drives more conversions, providing data-driven insights to improve your website or app.
2. Control group
The control group is the group that sees the original version of the web page or app. This group’s performance is used as a benchmark to compare against the performance of the variant group.
3. Variant (treatment group)
The variant, or treatment group, sees the new version of the web page or app. This group’s behavior is compared to the control group to determine the impact of the changes.
4. Hypothesis
Your hypothesis is a clear, testable statement predicting the outcome of your A/B test.
It usually follows this format: “If we change [specific element], then [desired outcome] will happen.”
Crafting a solid hypothesis is essential for a successful experiment.
5. Experiment design
Experiment design involves planning your A/B test.
This includes defining your hypothesis, selecting the metrics you’ll track, determining the sample size, and setting the duration of the test.
A well-designed experiment ensures reliable results.
6. Randomization
Randomization means randomly assigning participants to either the control or variant group.
This process minimizes biases and ensures that any observed effects are due to the changes you’re testing, not external factors.
7. Sample size
Sample size refers to the number of participants in your A/B test. A larger sample size increases the reliability of your results, making it easier to detect true differences between the control and variant groups.
8. Statistical significance
Statistical significance indicates that the results of your test are likely not due to chance.
It provides confidence that the observed effect is real and not just a random occurrence. This is crucial for validating your test results.
9. P-value
The p-value helps determine statistical significance by measuring the probability that the results of your A/B test occurred by chance.
A p-value of less than 0.05 is typically considered statistically significant, meaning there’s less than a 5% probability that the results are due to random variation.
10. Confidence level
The confidence level indicates how certain you can be that your results are reliable.
A 95% confidence level means you can be 95% sure that the observed differences are real. Higher confidence levels provide greater assurance in your findings.
11. Conversion rate
Conversion rate is the percentage of users who complete the desired action, such as making a purchase or signing up for a newsletter.
It’s a key metric for measuring the success of your A/B test and overall campaign performance.
12. Lift
Lift refers to the percentage increase in the conversion rate of the variant group compared to the control group.
It’s a direct measure of the impact of your changes, showing how much better (or worse) the variant performed.
13. Metrics
Metrics are the data points you track to measure the success of your A/B test. Common metrics include conversion rate, bounce rate, and average order value.
Selecting the right metrics is vital for accurate and meaningful test results.
Understanding user behavior through these metrics helps you make data-backed decisions for website optimization.
14. Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis involves applying statistical methods to interpret the results of your A/B test. This process helps you understand the significance, reliability, and implications of your findings.
Tools such as t-tests, chi-square tests, and regression analysis are often used to analyze test data.
Advanced terminology
Now that you have a handle on the basics, it’s time to delve into more advanced concepts. These terms will help you refine your testing strategies and understand more complex scenarios.
15. Multivariate testing
A multivariate test goes beyond A/B testing by comparing multiple variables and their interactions simultaneously.
This approach helps identify the best combination of changes to optimize performance, providing more comprehensive insights than simple A/B tests.
16. Bayesian vs. frequentist approaches
These are two different statistical methods for analyzing A/B test data. The frequentist approach focuses on long-run frequency properties, while the Bayesian approach incorporates prior knowledge and updates beliefs based on new data.
Each method has its strengths and can be chosen based on the specific needs of your test.
17. False positives and false negatives
A false positive occurs when you incorrectly conclude that a change has an effect when it doesn’t. A false negative happens when you fail to detect an actual effect.
Minimizing these errors is crucial for accurate A/B testing.
18. Statistical power
Statistical power is the probability that your test will detect an effect if there is one. Higher statistical power reduces the risk of false negatives and increases the reliability of your results.
You need adequate statistical power to draw meaningful conclusions from your tests.
19. Test duration
Test duration is the length of time your A/B test runs. It needs to be long enough to gather sufficient data but not so long that external factors influence the results.
Finding the right balance is key for obtaining accurate results. Analyzing the duration and results of past tests can provide valuable insights for optimizing future tests.
20. Segmentation
Segmentation involves dividing your audience into distinct groups based on characteristics like demographics or behavior.
This allows you to analyze how different segments respond to your variants, providing deeper insights into the effectiveness of your changes.
Segmenting your audience helps you tailor tests to meet the specific needs and preferences of your target audience.
21. Interaction effects
Interaction effects occur when the effect of one variable depends on the level of another variable. Recognizing these can help you understand the combined impact of multiple changes, ensuring more precise optimizations.
22. Regression to the mean
Regression to the mean is a statistical phenomenon where extreme measurements tend to return to average levels over time. Being aware of this helps prevent you from misinterpreting natural variations as real effects.
23. Holdout group
The holdout group is a subset of users deliberately excluded from the test to serve as a baseline for future comparisons. It helps validate the long-term impact of your changes.
Top 5 A/B testing tools and platforms
Now that you’re familiar with the terminology, let’s look at some tools that can help you run effective A/B tests.
1. OptiMonk
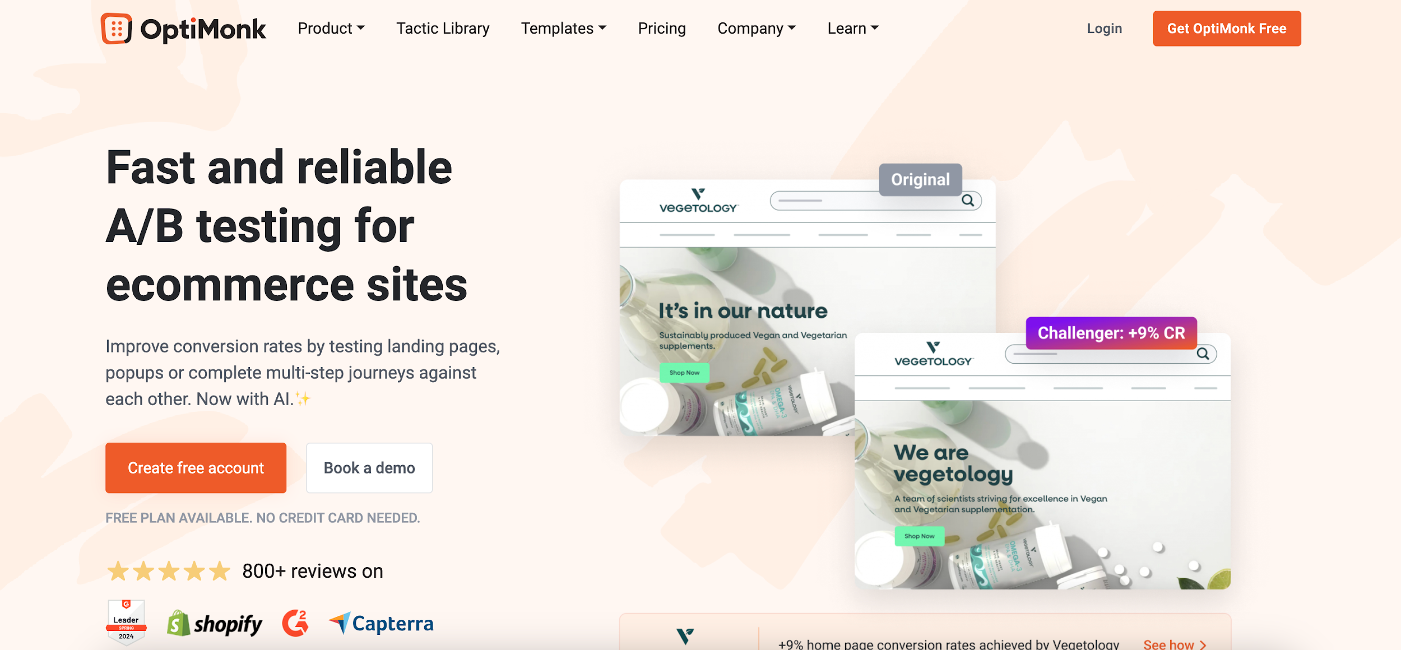
OptiMonk is an all-in-one conversion rate optimization (CRO) toolset designed specifically for ecommerce marketers and agencies. It offers a suite of features, including popups, website personalization, and A/B testing.
OptiMonk allows you to test new elements on your website to understand their impact on user engagement and satisfaction.
Key feature #1: Visual editor
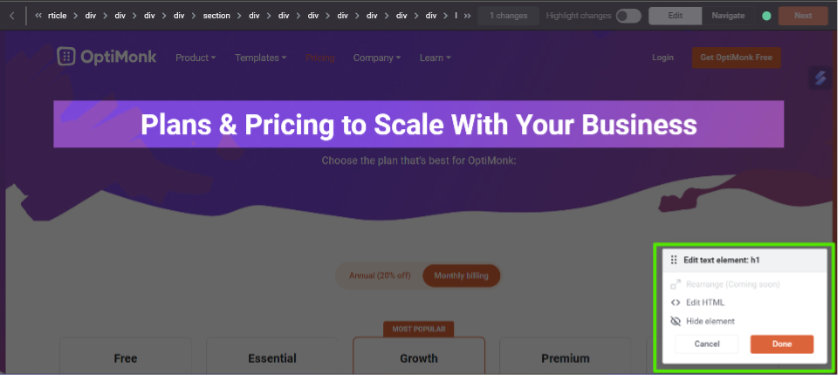
OptiMonk’s visual editor is a game-changer for anyone looking to test landing page variations without coding skills. It allows you to quickly set up and run A/B tests on page elements such as headlines, product descriptions, or calls-to-action.
Key feature #2: Targeting
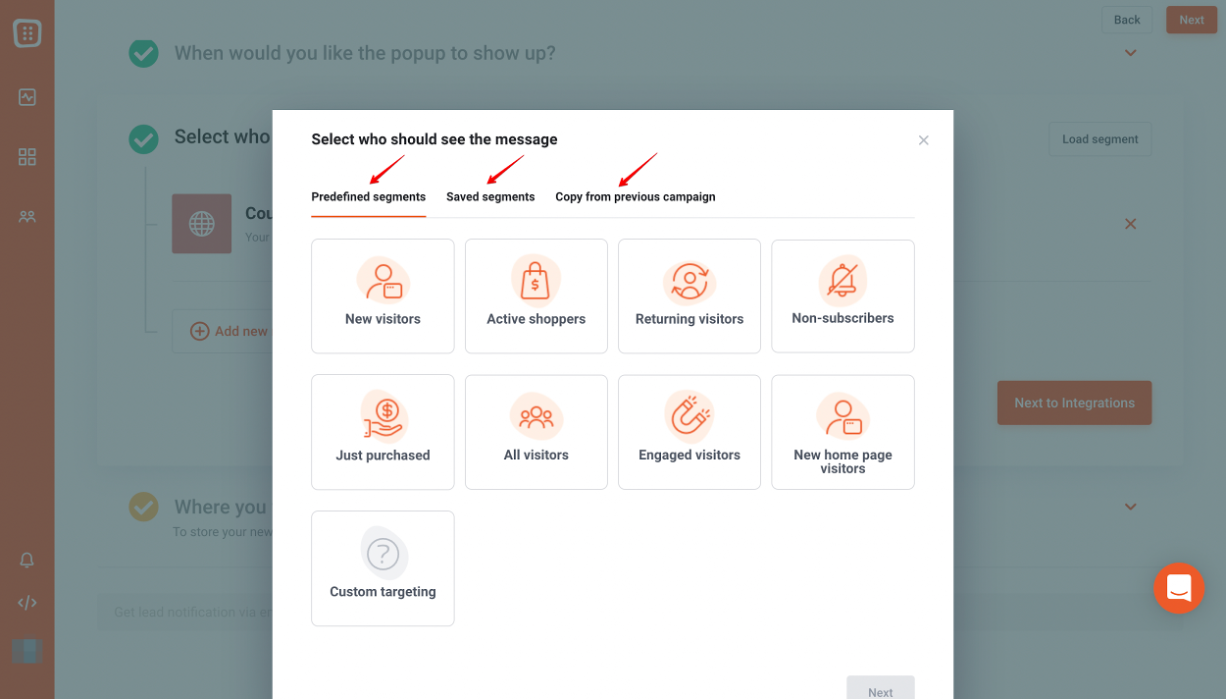
Advanced targeting is key for meaningful A/B testing, and OptiMonk excels in this area. The tool enables you to create segments based on factors like traffic source, device type, and visitor behavior, ensuring relevant and actionable results.
Key feature #3: Analytics
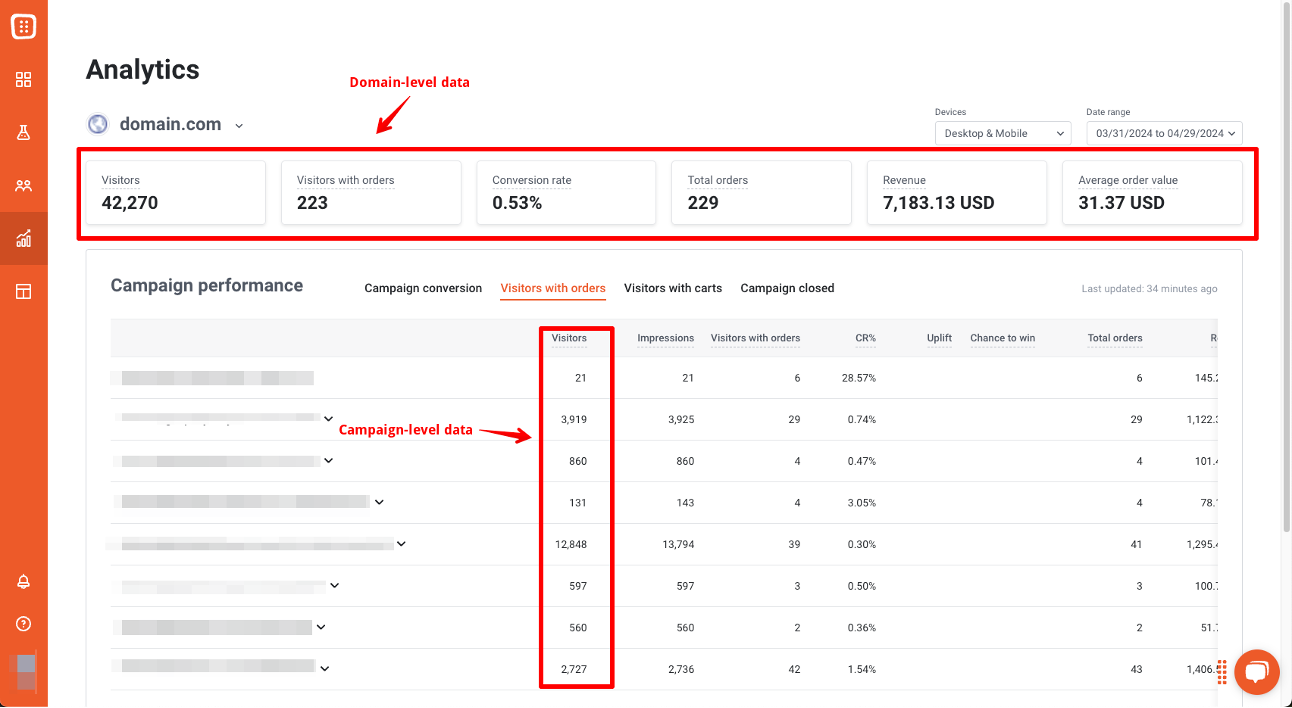
Understanding the impact of your tests is crucial, and OptiMonk provides robust analytics to help you track revenue, orders attributed, and custom metrics. These insights allow you to make data-driven decisions to refine your marketing campaigns.
Pricing:
OptiMonk offers a free plan for smaller businesses, with paid plans starting at $29 per month.
For more details, visit our A/B Testing page.
2. Optimizely
Optimizely is designed to power your entire marketing lifecycle, enabling your team to create content quickly and launch experiments with confidence. It brings together collaboration, design, and execution to maximize efficiency and innovation.
Key features:
- Collaboration: Shared workspaces for crafting hypotheses and testing variations.
- User-friendly editor: Easily target and preview changes to any web page element.
- Speedy execution: Dynamic traffic adjustments to top-performing variations for fast, statistically sound results.
Pricing:
For pricing information, you’ll need to request a quote from their sales team.
3. VWO
VWO is a comprehensive web experimentation platform designed to optimize the entire customer journey. It allows you to create multiple variations and analyze visitor behavior to enhance user experiences and drive sales.
Key features:
- Visual and code editor: Make quick edits with the visual editor or implement complex changes using the code editor.
- Fast, secure, and private: Ensures high performance with robust data protection.
- Integration: Seamless integration with external data sources for precise targeting.
Pricing:
VWO offers a free plan. Paid plans start from $190 per month.
4. Adobe Target
Adobe Target is a sophisticated A/B testing and optimization platform designed for personalized customer experiences. It leverages AI-powered testing, personalization, and automation to cater to individual needs.
Key features:
- Mass personalization: Scales omnichannel personalization efficiently.
- Ease-of-use: Simple setup and testing for quick insights.
- AI-driven personalization: Apply AI for tailored visitor experiences.
Pricing:
For pricing information, you’ll need to request a quote from Adobe Target’s sales team.
5. AB Tasty
AB Tasty is a digital experience optimization platform that combines advanced testing capabilities with intuitive experience-building tools. It’s ideal for businesses aiming to reach their conversion goals swiftly.
Key features:
- Variety of testing options: Run A/B tests, split tests, multivariate tests, and more.
- Intuitive interface: User-friendly design for creating impactful experiences.
- Custom widgets: Create dynamic widgets to capture user attention.
Pricing:
To get pricing information, you’ll need to request a quote from AB Tasty’s sales team.
Wrapping up
Understanding A/B testing terminology is crucial for running successful experiments and making data-driven decisions.
With this glossary, you’re now equipped to navigate the world of A/B testing with confidence.
Remember, each term plays a vital role in the overall process, and mastering them will help you optimize your marketing strategies effectively.
Wanna get started with the best A/B testing tool today? Try OptiMonk!
Happy testing!
Migration has never been easier
We made switching a no-brainer with our free, white-glove onboarding service so you can get started in the blink of an eye.
What should you do next?
Thanks for reading till the end. Here are 4 ways we can help you grow your business:
Boost conversions with proven use cases
Explore our Use Case Library, filled with actionable personalization examples and step-by-step guides to unlock your website's full potential. Check out Use Case Library
Create a free OptiMonk account
Create a free OptiMonk account and easily get started with popups and conversion rate optimization. Get OptiMonk free
Get advice from a CRO expert
Schedule a personalized discovery call with one of our experts to explore how OptiMonk can help you grow your business. Book a demo
Join our weekly newsletter
Real CRO insights & marketing tips. No fluff. Straight to your inbox. Subscribe now
Nikolett Lorincz
- Posted in
- Conversion
Partner with us
- © OptiMonk. All rights reserved!
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
Product updates: January Release 2025








